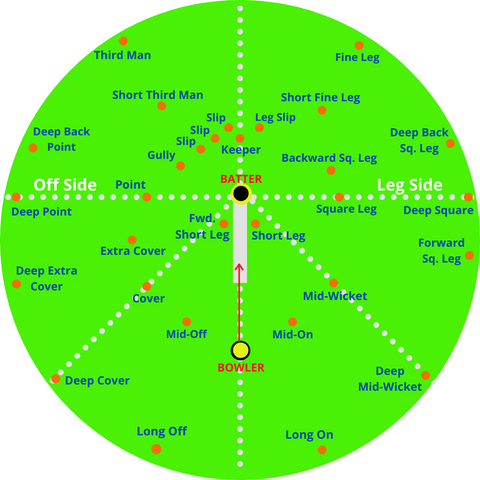
Cricket Fielding Positions
Cricket Fielding Positions are at the strategic heart of the game.
Join us as we delve into how a captain’s tactical field placements can dramatically shape the outcome of a match, influenced by the type of game, pitch conditions, and the unique tendencies of players.
We've watched thousands of days of cricket here at Australian Cricket Tours so believe me - we know just how important "setting the field" can be!
List of Normal Cricket Fielding Positions
Regular or Orthodox Field Positions At The Start Of A Match May Include:
- Wicketkeeper
- Third Man
- Slips
- Gully
- Point
- Cover
- Mid-Off
- Mid-On
- Mid-Wicket
- Square Leg
- Fine Leg
- Short Leg (Bat Pad)
List of Other Cricket Fielding Positions
Variable Field Positions Once The Match Develops May Include:
- Short Third Man
- Extra Cover
- Forward Short Leg
- Deep Backward Point
- Deep Point
- Deep Extra Cover (Sweeper)
- Deep Cover (Sweeper)
- Long-Off
- Long-On
- Deep Mid-Wicket
- Deep Forward Square-Leg
- Deep Square Leg
- Backward Square Leg
- Deep Backward Square Leg
- Leg Slip
- Short Fine Leg
Cricket Fielding Strategies
Fielding positions for one of the more complex ball sports have not so much become more complex as more varied and obscure than those of yesteryear, if not yesterday.
Using just 10 fielders to save the bowler’s figures and possibly career, the captain’s ability to position his field across a vastly variable area is a skill.
The fielding captain needs to limit the numbers of runs conceded by ‘pre-empting’ where the batsmen will likely (or accidentally) hit the ball, to either 1; prevent the batter scoring, or 2; catch the ball should it be hit in the air, in which case the batter is out.
This skill mirrors the art of the batter whose craft is to hit the ball to where there is no fielder, and thus allow the opportunity to score more runs.
Test Cricket, ODI, or T20 will determine how the game starts but for this we focus on Test Cricket, that usually starts with, in cricket parlance, an ‘orthodox’ field.
Our picture shows ALL ‘normal’ fielding positions, and not a game starting with 31 persons on the field, when all formats start with 10 fielders and one bowler.
As orthodox as our image is, there is often a time toward the end of a Test Match when 10 fielders are in a ‘ring’ around the batter, in catching positions (slips/short leg/leg slip).
When this happens, forget the positions shown.
10 fielders around the batter are all there to apply pressure, and duly take a catch off the remaining batter/s to win the Test.
Starting a Test Match, you normally see a wicket-keeper (keeper), 2-3 slips, a gully, point, cover, mid-off, mid-on, mid-wicket, square leg, and fine-leg or third man, depending on how many slips you have.
The fielding positions are affected by who is batting and who is bowling. Different positions for different players, and the captain’s ‘mind’ on how they believe they can get the batter out.
Slips & Gully Fielders Work Together
You often see 3 or more slips at the start of a game to catch the ball from the offside edge of the bat, at a time when the batter is adjusting their eyes to speed and bounce of the ball.
The number of slips, along with sometimes 2 gully fielders, will depend on the bowler’s style and delivery.
This many positioned in what is termed ‘the cordon’ to catch the ball off the edge suggests the ball will be bowled on that side of the batter. Thus, you wouldn’t need square leg, fine leg or even third man (usually the fielder bowling from the other end) who often comes into the slips.
The term in cricket is ‘bowling to your field’. This means if you have 7 or 8 men on the off-side, you do not bowl the ball on the legside (or wider) allowing the batter to hit the ball to where there are fewer fielders.
I have bowled in a game, representing Australia House Cricket Club in London, with 9 fielders on the off-side. The batter still managed to hit 2 boundaries on the off-side, though 2 catches were also dropped, but I digress from failed glory.
The field can change ball-by-ball, pending the batters’ scoring endeavour. With the field changing to outsmart the batter, the batter may also pre-empt what type of or where the ball will be bowled. This is where the art of batting, bowling, and captaining is best displayed.
Often the batter pre-empts the ball to be bowled based on where the fielders are positioned. Batters often tell themselves, ‘if it is this type of ball, don’t hit the ball there’.
Disappointingly, they often can’t resist the temptation to hit the ball to exactly where they said they wouldn’t, or are forced into a mistake because the ball wasn’t what they expected and are dismissed.
It is a game of chess on an open field, all players anticipating what the other players will do and making a move based on that.
The bottom-line is, 9 fielders and one wicket-keeper can be positioned anywhere the Captain wants.
Cricket Fielding Zones
Cricket fielding is largely categorised into three zones:
-
Close Infield: Positioned near the batsman, these fielders aim to take quick wickets through close catches. This zone includes slips and positions like silly point and short leg, ready to catch any edged balls.
-
Infield: In limited-overs cricket, marked 30 yards from the wicket, infielders focus on stopping runs. Their role shifts from preventing singles to blocking boundary hits depending on the match's pace and strategy.
-
Outfield: Situated along the boundary rope, outfielders primarily prevent fours and sixes. They are also pivotal for catching misdirected or powerfully hit shots that travel far.
Video Analysis of All Cricket Fielding Positions
Cricket Fielding Position Madness (Witnessed First Hand)
I have even bear witness to 9 slips, Australia vs Zimbabwe in Harare 1999, 2nd ODI; Damien Fleming to David Mutendera who safely let the ball pass through to the keeper, while uninterested Andy Blignaut, leaning on his bat at the non-striker’s end, kept the umpire company.

In the modern-era plagued with ODI and T20 cricket that requires sublime thinking outside the box, Test Cricket now and then sees unorthodox positions.
Abu Dhabi 2014 saw Australia Captain Michael Clarke position a fielder directly behind the umpire about halfway to the boundary. No name for that position except ‘different’.
To a lesser degree, Australia vs West Indies at the Melbourne Cricket Ground, 2000, there were 8 fielders on the offside with a lone Colin ‘Funky’ Miller at mid-on. It depends on the state of play, batters, bowlers, and the will to try anything to get a wicket, albeit by sheer dumb luck.
That’s today’s game but let’s cast our mind (or Google) back to Sir Donald Bradman who ended his Test career with an average of 99.94, or 6996 runs from 70 trips to the middle.
If you could look at footage of Bradman as easily as you can see replays of today’s game, you may find that throughout every inning, the field rarely changed.
There would always be 2-3 slips, gully, point, cover, etc… As such, where was the challenge or pressure applied by the field to force a mistake? It made Bradman’s job infinitely easier knowing the field was always in the same position.
One exception was the ‘Bodyline Series’ of 1932-33, when England Captain Douglas Jardine thought ‘outside the box’ for the first time, but that’s a different story.
This is not saying had the field been rotated and served drinks as often as today Bradman may not have scored the same number of runs. The man was a freak. Defined by the fact that had any other batsman been anywhere near as good, they too may average 99.94 against the same never-changing field.
Fast-forward to today, you often need to push pause on the game to know what’s happened before the field changes again.
With that, though this is oriented to Test Cricket, proliferation of money-spinning white-ball bi-lateral & franchise cricket, sees batters changing, adapting, and developing their skill-set match-by-match.
Their ability to hit the ball in any direction no matter what ball is delivered or where the field is placed, is mind-boggling.
Cricket Fielding Positions: Our Final Thoughts
What is also 'curious' (for me!), in the latter stages of the 2nd inning of a T20 (more than ODI's) when a team is trying to restrict runs to win the game, is why the wicket-keeper is never positioned on the boundary in front of the sightscreen?
So many runs are scored, so many games won & lost by balls hit over the keeper’s head (in an orthodox position), wouldn’t it be worth conceding the guaranteed single, or even wicket, to save the boundary?
Thanks for reading everyone! We hope you enjoyed our take on Cricket Fielding Positions and managed to get something out of the article.
Why not consider reading this article on the Types of Ducks in Cricket next!
Cricket Fielding Positions: Other FAQs
-
What determines the initial fielding setup at the start of a cricket match?
Initial setups are influenced by the bowler's style, pitch conditions, and the batsman's weaknesses, with placements like slips and close infielders arranged to exploit early game conditions. -
How do fielding positions vary between different formats of cricket? Test cricket features more defensive and spread-out positions to control runs over long periods, while ODI and T20 setups are more dynamic and aggressive to restrict scoring and take quick wickets.
-
What are the most common fielding changes a captain might make during a match? Captains adjust fielders based on the batsman's play, bowler's strategy, and match progress, such as moving fielders to the boundary during powerplays or closer to the bat to seek wickets.
-
How does a team prepare for fielding before a cricket match? Teams engage in drills focusing on agility, catching, and throwing, including slip catching and boundary fielding, to simulate and respond effectively to match conditions.
-
Are there any unconventional fielding positions that have proved surprisingly effective in international cricket? Occasionally, positions like the 'fly slip' or a fielder behind the bowler are used to catch batsmen off-guard and disrupt their focus, tailored to specific match scenarios or player skills.
